Making computers faster and more powerful is something that companies have always been aiming for. However, quantum computing is the one idea that could take that to the next level. Processing power has reached a point where it cannot go much higher without breaking the quantum barrier, and breaking that barrier would be a huge step leading to benefits for all of society. Many companies have been working to break that barrier as quantum computing emerges.
Key Facts About Quantum Computing
Quantum computing aims to develop computer technology based on quantum theory, which explains the properties and behaviors of matter on the atomic level and below the atomic level (sub-atomic or quantum level). So, quantum computing tries to take advantage of the strange behaviors exhibited by matter at the quantum level. We already know that the computers we use today perform calculations using binary “bits” composed of one and zero, but quantum computers use quantum bits (qubits) which can exist in both states at the same time, along with other states in between.
For that reason, qubits have the property of quantum entanglement, which means that groups of particles depend on each other and cannot be described independently. These groups of particles could, theoretically, be an unlimited distance apart, but scientists have found that if they are linked by quantum entanglement, they are able to transfer information between each other. Using this knowledge, computer scientists have been working to take advantage of this and build a quantum computer that is much more efficient than the conventional computers we know today.
First Quantum Computers
In 1982, the idea of quantum computing was first proposed. Since then, the idea has been used to crack encryption standards, and for a quantum network. The first commercial business, 1Qbit, was also established in 2012. Recently, all of this time and dedication to quantum computing has brought results. In 2016, IBM launched Q via cloud which offered 5 qubit quantum computing services. It upgraded to 20 qubits last year which greatly improves processing power. Now, other companies have been getting in on the action. Google, NASA, and Lockheed Martin have been taking advantage of D-Wave’s quantum computing infrastructure while Alibaba and Baidu work to create their own.
Alibaba and Baidu Enter the Race
Alibaba just released an 11 qubit quantum computer to the market that makes it the second quantum computer. Still, it doesn’t beat the 20 qubit system IBM has. Many of the details of Alibaba’s system have not yet been released, but its emergence into the race for quantum computers shows that bigger and better things are coming.
Shortly after Alibaba, Baidu announced its own launch of an institute for quantum computing which will be dedicated to the application of quantum computing software and information technology. The institute will be headed by Professor Duan Runyao, who says he plans to turn it into a world-class institution within five years.
During those five years, Baidu’s plan is to have quantum computing gradually integrated into the business. The fact that quantum computing will become such a huge part of Baidu’s business shows that they are eager to compete. Neither these companies or IBM are close to the scale of D-Wave, but they can only gain knowledge and improve from these first trials.
D-Wave
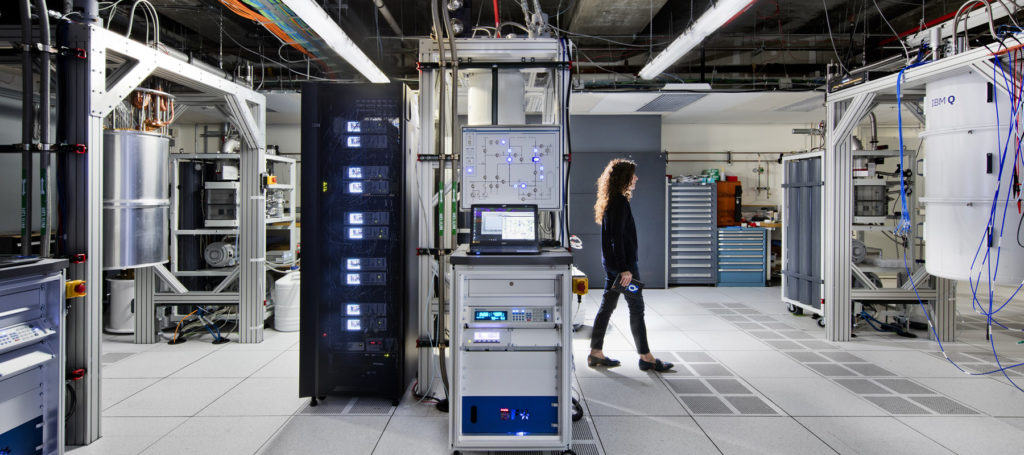
The huge potential of quantum computing brings huge players into the competition to create a quantum computer. D-Wave has been working on quantum computing for eight years, developing a processor that has been used only in research labs. The company recently received a $50 million investment, so it plans to move into the public cloud soon. This is the next step as D-Wave’s technology has already been used by researchers at other companies for years.
In 2015, Google and NASA worked together on a project using a D-Wave machine – they said it performed tasks 100 million times faster than the processors on conventional computers. D-Wave machines have been used by Google, NASA, and Lockheed Martin for other experiments, such as; seeing if quantum computers can solve problems in drug discovery, cyber-security, and space exploration. Even in research alone, quantum computing has an abundance of benefits, but it would also benefit the public greatly.
According to D-Wave’s CEO Vern Brownell, the company’s technology will be available in the public cloud for the first time this year by either Amazon, Microsoft or Google. He says he want to be, “…an arms merchant for the cloud providers” because, “…once one of them has the capability, all of them will want to have it”. D-Wave is driving the hardware forward and letting other companies use the hardware for applications and software tools.
D-Wave is in a great position; they have been working on quantum computing for so long that they have a huge lead on any other company. Therefore, they can provide all of the resources to huge companies like Amazon, Microsoft, and Google.
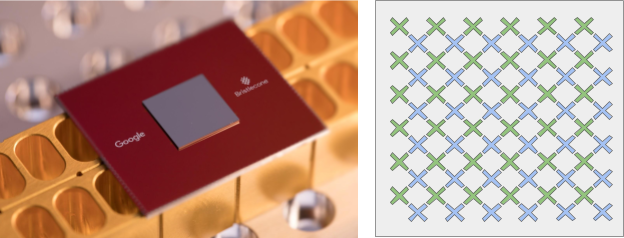
Google’s Quantum Computer Chip
However, while D-Wave creates machines, Google has also been developing its own chip. This quantum computer chip is called Bristlecone and it is composed of 72 qubits. This will go far above and beyond the 9 qubit device they already made, and any problems they had with that device should now be worked out. Google plans to use quantum computing for physics and chemistry simulations along with artificial intelligence chores. Since AI is something Google is very invested in, quantum computing will directly benefit the company in that way.
Quantum Computing for Everyone
Ideally, quantum computing will improve to the point where everyone can enjoy and benefit from it, not just companies and computer scientists. Right now, quantum computers are far too complex and expensive to be commercialized. Although D-Wave has open-sourced its software, that only allows people to work with it and solve problems at the software level. They won’t have a quantum computer to actually use the software.
Now, companies must work to make quantum computers more economical, or at least have specific, useful tasks that only they can perform. Quantum computers are technically “here”, but they are not here for everyone yet. The potential is incredible. However, commercializing quantum computers could still be a ways off.